
Academic Handbook Course Descriptors and Programme Specifications
BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions Programme Specification
Last modified on October 15th, 2024 at 3:31 pm
| Awarding Body | Northeastern University – London |
| Teaching Institution | Northeastern University London |
| Apprenticeship Standard | Digital and Technology Solutions Professional (Integrated Degree) ST0119 |
| Relevant QAA Benchmark Statement | Computing (March 2022) |
| HECoS | 100367
100078 |
| QAA Framework for Higher Education Qualification Level | Honours Level 6 |
| Final Award | BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (Software Engineer)
BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (IT Consultant) BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (Business Analyst) BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (Cyber Security Specialist) BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (Data Analyst) |
| Exit Awards | CertHE Digital and Technology Solutions
DipHE Digital and Technology Solutions |
| Programme Code | LBSDTS-A |
| Approved Start Dates | October 2023 |
| Language of Instruction | English |
| Language of Assessment | English |
| Mode of Study | Part-time blended learning; work-based learning |
| End-Point Assessment | Integrated (30 credits) |
| End-Point Assessment Organisations | Northeastern University London |
Programme Overview
Apprenticeships extend learning beyond the classroom and into the workplace. The aim is to integrate academic learning at degree level with on-the-job practical training to provide a holistic programme of education and training to meet the skills needs of employers now and in the future.
This Degree Apprenticeship programme will develop professional practice, contextualised in the workplace using industry standard technologies and approaches that are shaped by modern businesses. Apprentices studying on this programme are employed by an employer (hiring business) and are working in an Information Technology role.1
The apprentice (learner) will study with Northeastern University London (the University) (the provider) for approximately 60 days a year (or stage) for the duration of the three-year programme. This equates to approximately one day per week for 42 weeks each year. In addition, they will participate in up to three five-day ‘bootcamps’ in any given year. Learners must complete the required amount of off the job training hours which equates to a minimum of 6 hours per week on average. Learners must complete the minimum required hours to complete the apprenticeship. Additionally, the learner and employer will commit to a further two days per week, for 42 weeks each year, for provider-guided work-based training.
The programme has five distinct routes (specialisms) – Software Engineer, IT Consultant, Business Analyst, Cyber Security Analyst and Data Analyst. Learners will study 120 credits per year (1200 nominal learning hours) and will be considered part-time learners by the University. Each course, typically 15 credits, is assessed by a range of activities aligned to industry norms, i.e. almost all assessments relate to workplace activities that are expected in a technology-related occupation. The content, and consequently the learning outcomes and methods of assessment, vary between courses. Where possible, assessments will be undertaken in the workplace. The programme begins with ‘Business Fundamentals’ to introduce and familiarise learners with the contemporary world of business and is followed by an exploration of the fundamental ideas of programming principles in ‘Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming I’. The programme then introduces ‘Mathematical Structures and Methods’ that form the foundation of computer science,, before introducing ‘Data Management Systems’ which explore how utilising information and leveraging IT can contribute to the diverse success of a broad range of enterprises. The subsequent ‘Database Design & Management I’ course examines data design and structures, and learners learn how to query and manipulate data before applying their learning and further exploring more advanced programming principles in ‘Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming II’. Learners then study what drives the behaviour of individuals and teams in ‘Organisational Behaviour’, seeing how improving business processes and preparing the workforce can make the most efficient and effective use of any information systems deployed. At or close to the end of the first year, there is a two-week intensive course, exploring ‘Digital Fluency in the AI-enabled Enterprise’. Throughout Year 1, core knowledge is contextualised using industry-recognised cloud-based platform technology (and solution) training embedded through the courses, resulting in industry certification where applicable.
Year 2, or Stage 2, begins with an ‘IT Project Management’ course covering all aspects of the project lifecycle including tools and techniques. ‘Database Design and Management II’ explores advanced data management issues and implementing a database schema. The programme also contains opportunities to learn how to program utilising software used in ‘Data Analytics’ solutions and to explore the ‘Cyber Security’ issues affecting organisations including the significance, risk and impact of ensuring IT systems are secure and compliant. ‘Information Technology Service Management’ equips learners with the skills to examine the frameworks and strategic approaches for the life cycle management of IT products. Learners also cover the history of multimedia technology and its uses in ‘Visual Communication of Information’. Building on their understanding of data, they will learn techniques of ‘Data Visualisation’ to manipulate and present various types of business data to stakeholders. As with Year 1, there is a two-week intensive course where learners will be introduced to ‘Networks and Platform Technologies’, exploring the fundamentals of IT networks. Like in Year 1, Year 2 core knowledge is contextualised using industry-recognised cloud-based platform technology (and solution) training embedded through the courses, resulting in industry certification where applicable.
Year 3, or Stage 3, is where learners select a specialism (Software Engineer, IT Consultant, Business Analyst, Cyber Security Analyst or Data Analyst) and courses covered will depend on the selected specialism with all 5 pathways finishing with a work-based project and a portfolio, which contributes to the end-point assessment (EPA).
Structure of the Digital and Technology Solutions Programme (360 Credits)
The apprenticeship is taught at undergraduate level. As per the apprenticeship standard, there are five specialisms, chosen and realised in Stage 3. The recommended order in which the courses will be taken is shown in Appendix D.
Stage 1 (Level 4)
Compulsory Courses
NCHNAP443 Business Fundamentals (15 credits)
NCHNAP444 Mathematical Structures and Methods (15 credits)
NCHNAP445 Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming I (15 credits)
NCHNAP446 Data Management Systems (15 credits)
NCHNAP447 Database Design and Management I (15 credits)
NCHNAP448 Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming II (15 credits)
NCHNAP449 Organisational Behaviour (15 credits)
LCSCI4273A Digital Fluency in the Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Enterprise (15 credits)
Stage 2 (Level 5)
Compulsory Courses
NCHNAP555 Information Technology Project Management (15 credits)
NCHNAP556 Database Design and Management II (15 credits)
NCHNAP558 Data Analytics (15 credits)
NCHNAP557 Data Visualisation (15 credits)
NCHNAP559 Visual Communication of Information (15 credits)
NCHNAP560 Information Technology Service Management (15 credits)
LCSCI52100A Cyber Security (15 credits)
LCSCI5299A Networks and Platform Technologies (15 credits)
Stage 3 (Level 6)
Select one specialism
Software Engineer Specialism
NCHNAP6140 Object-Oriented Design and Development (15 credits)
NCHNAP688 Software Engineering (15 credits)
LSCI62118A Software and Data Security (15 credits)
NCHNAP6139 Agile Software Development (15 credits)
LCSCI62106A Advances in Software Engineering (30 credits)
LSCI62119A Software Engineer End-Point Assessment (30 Credits)
or
IT Consultant Specialism
NCHNAP685 Consulting Fundamentals and Frameworks (15 credits)
LISYS62113A Customer Life Cycle Management (15 credits)
NCHNAP687 Advanced Information Technology Service Management (15 credits)
LISYS62112A Business and Change Management (15 credits)
LISYS62107A Theory and Practice of Business Technology Consultancy (30 credits)
LISYS62111A Information Technology Consultant End-Point Assessment (30 Credits)
or
Business Analyst Specialism
NCHNAP685 Consulting Fundamentals and Frameworks (15 credits)
NCHNAP688 Software Engineering (15 credits)
LCSCI62114A Predictive Analytics Using Programming (15 credits)
LISYS62112A Business and Change Management (15 credits)
LISYS62104A Advanced Topics in Business Analysis (30 credits) and
LISYS62108A Business Analyst End-Point Assessment (30 Credits)
or
Cyber Security Specialism
LCSCI62117A Data and Network Protection (15 credits)
NCHNAP688 Software Engineering (15 credits)
LSCI62118A Software and Data Security (15 credits)
LISYS62116A Enterprise Security Management (15 credits)
LCSCI62105A Advanced Topics in Cyber Security (30 credits)
LCSCI62109A Cyber Security Analyst End-Point Assessment (30 Credits)
or
Data Analyst Specialism
LDSCI62115A Data Driven Decision Making (30 credits)
LCSCI62114A Predictive Analytics Using Programming (15 credits)
NCHNAP691 Implementing Data Science (15 credits)
LDSCI62103A Advanced Topics in Data Analytics (30 credits)
LISYS62110A Data Analyst End-Point Assessment (30 Credits)
Entrance Requirements
The learner will need to apply for a degree apprenticeship role within a hiring business, or already be in employment with responsibilities to be aligned with the degree content.
Entry requirements are agreed then set, based on numerous factors including availability of additional on-the-job support, by both the employer and provider. As such, entrance requirements may vary between apprenticeships. Learners are selected based on their application, an interview and an assessment process which is tailored to the learner’s apprenticeship position.
Typically, employers require:
- Three A levels (or equivalent at BBB or above)
- At least Grade 4/C GCSE mathematics, English and IT
Some applicants may not have traditional qualifications as listed above, and have prior learning and skills developed from the workplace, these will be considered on a case-by- case basis.
Learners will also need to meet the government’s eligibility criteria:
- Have been a UK/EU/ESS resident for the past three years or more prior to starting the programme.
- Have left full-time education prior to the start date of the apprenticeship.
- Be aged at least 16 years old to meet government funding criteria.
Recognition of Prior Learning
Where a learner is eligible to apply for the recognition of prior learning on the basis of certificated or experiential learning, this will be considered in the Initial Needs Assessment, as per Education Skills and Funding Agency (ESFA) Funding Rules, and will take due consideration of the University’s Recognition of Prior Learning and Credit Transfer Policy.
Aims of the Programme
The overall aim of the programme is to:
- Offer specialist degree-level study that underpins the Level 6, Digital and Technology Solutions Professional (Integrated Degree) apprenticeship.
- Offer a programme of study that meets the needs and expectations of businesses and organisations and supports the career development of digital and technology solutions professionals.
- Provide flexible and broad access to an incrementally structured learning experience that is designed to encourage and enable a diverse range of learners to work within a range of organisations and businesses.
- To support the development of digital and technology specialist skills that will be valued and supported within work-based contexts, i.e. the development of technology enabled solutions for both internal and external customers, in a range of areas including software, business, and data infrastructure.
- Place the specialist study of digital and technology solutions within a broad contextual framework; provide learners with an understanding of the role played by digital and technology solutions professionals and how their specific and transferable knowledge and skills are applied in a range of professional contexts.
- Develop a good understanding of the principles, theories and technologies that enable the professional practice of digital and technology solutions professionals.
- Provide learners with a rich and varied academic experience that is designed to support the integration of theory and practice within the workplace.
- Instil a strong professional work ethic that encourages independence, empathy and a strong awareness of ethical, legal and social issues that pertain to the role of digital and technology solutions professionals.
- Encourage and support self-determined, independent, critical self-reflection and advanced communication skills.
- Develop a high standard of written English, mathematics and presentation skills.
- Blend the development of business, mathematical, computing and technical understanding with a raft of related transferable skills that enable learners to develop their careers and operate successfully as Digital and Technology Solutions Professionals within a range of professional contexts.
- Provide learners with the ability to implement technology solutions that enable organisations and businesses to develop new products and services and to increase productivity using digital technologies.
Programme Learning Outcomes
A learner will be able to:
Knowledge and Understanding
Note: for Specialism-specific Knowledge Learning Outcomes, please see the Apprenticeship Standard.
Subject Specific Skills
Note: for Specialism-specific Skills Outcomes, please see the Apprenticeship Standard
Transferable and Professional Skills
All of the above learning outcomes are mapped to the relevant QAA Subject Benchmark threshold statements and Apprenticeship Standard.
Teaching and Learning Strategies
Strategies
The apprenticeship is studied through blended work-based learning, over a 3-year period, and is delivered through the online interactive virtual learning environment (VLE).
The achievement of the programme learning outcomes is supported primarily through an extensive range of e-learning interactions and materials. Delivery methods include:
- Lectures (synchronous face-to-face or online as well as pre-recorded)
- Seminars for small group discussion (including online discussion)
- Informal discussion groups (including online discussion)
- Assessments
- Links to related reading material
- Individual learning plans (ILP)
- Online presentations
- Participation in online forums
- Consolidation and revision sessions
- Independent study and research
- Final project
Regular in-depth formative feedback is provided to the learner, with advice and guidance to support their achievement in summative assessments. The programme aims to progressively enhance digital and technology knowledge and skills – as well as maths, English and communication skills – as they practise and apply their new found knowledge and skills in the workplace. Regular tri-partite reviews between the learner (apprentice), their apprenticeship advisor (provider) and workplace line manager (employer) formally monitor and evaluate the learner’s progress.
The blended-learning work-based programme ensures that learners have the opportunity to explore their subject in an incrementally structured, well-managed and appropriate manner. It develops the knowledge, core and subject-specific skills, and transferable skills, required by learners and enhances their confidence. The combination of academic study and work-based learning is a key feature of the apprenticeship. Practical and theoretical experiences in the workplace, in tandem with their academic studies, develop and enhance the learner’s specialist knowledge, skills and behaviours.
Assessment tasks increase in complexity and level of demand from Year 1 (or Stage 1), where introductory tasks assess the demonstration of knowledge, skills and abilities and establish the foundations of learning. Whereas, in the final year (stage) of the programme, the synthesis of advanced knowledge, understanding, critical thinking and professional skills, are assessed to meet the expectations of a degree-level apprenticeship.
Learners are supported to acquire and practise a wide range of transferable skills. These include problem solving, analysis, strategic thinking and interpersonal and communication skills. Learners will be effective team players within their work environments and fully participate in presentation work during their studies. Importantly, they are also encouraged to balance these cooperative interpersonal skills with responsibilities and self-development within the apprenticeship.
The programme is designed to progress steadily over the three years and develop learners’ conceptual sophistication through cumulative experience and knowledge. The final project will allow learners to develop their thinking in collaboration with an academic supervisor.
The University recognises and has embedded the expectations of current diversity, equity, and inclusion legislation, by ensuring that the programme is as accessible as possible by design.
Student Support and Development
Learners are strongly encouraged to inform the University of any medical conditions, disabilities, specific learning difficulties (SpLD) or neurological differences as soon as is practical. Students will be asked to submit supporting documentation from a doctor, clinical or educational psychologist detailing the nature of their disability and the impact it is likely to have on their studies in order to help us put in place appropriate support and accommodations. More information can be found in the Student Disability Policy. This data is managed and securely stored by Student Support and Development (SSD). At the start of the academic year, a number of talks and events are held which are designed to support and inform students with regard to mental health, disabilities, safety and learning support.
SSD meet with students as soon as possible, and preferably before the start of the academic year, to discuss their needs and draft a Learning Support Plan (LSP) which outlines the support to be provided both within the University (if appropriate) and externally. If requested by the student, the SDD will then arrange to inform relevant faculty of the student’s needs and any reasonable adjustments required.
If a student is undiagnosed but believes they may have a SpLD (e.g. dyslexia) the SDD will help them to access diagnostic services. If the assessment confirms a SpLD, the SDD will work the student in preparing a LSP and will provide advice about accessing additional funding and support through the Disabled Students Allowance, where a student may be eligible
For more information, please click here.
Assessment
Course are assessed in a variety of ways including:
Formative:
- Tests or quizzes
- Essays or reports
- Short answers and problem sets
- Oral presentations/debates/discussions
Summative:
- Computer-based examination
- Written/coding assignment
- Report
- Dissertation
- Oral assessment
- Presentation
- Practical skills assessment
- Set exercise
Appendix D contains the programme structure and assessment summary.
The assessment regulations can be found on the University’s website.
End-Point Assessment
The end-point assessment is integrated into the Digital and Technology Solutions Professional (Integrated Degree) apprenticeship as detailed in the Institute for Apprenticeships & Technical Education End-Point Assessment Plan. In summary, the apprenticeship culminates in the final project with presentation and a professional discussion underpinned by a portfolio. The final project is a substantial piece of work, typically taking around three months to undertake alongside the learner’s normal duties to their employer. It is this end-point assessment which will be judged against the standard, and test the skills, knowledge and behaviours together as applied in the workplace evidenced in the project and portfolio.
Awards
To be eligible for the award of an Honours degree, learners must obtain 360 credits, where 120 of which must be at Level 5, and 120 credits at Level 6.
Learners successfully completing Stage 1 of the programme who do not successfully complete Stage 2 will be eligible for the award of the Certificate of Higher Education (CertHE) in Digital and Technology Solutions. Learners successfully completing Stage 1 and Stage 2 of the programme who do not successfully complete Stage 3 will be eligible for the award of the Diploma of Higher Education (DipHE) in Digital and Technology Solutions.
Classifications
Learners are graded using Honours degree classifications for English universities, and follow the QAA (Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education) Code of Practice for the Assurance of Academic Quality and Standards in Higher Education.
The classification of the degree will be calculated using the method stated in the Academic Quality Framework Chapter 7.
Exemptions From Northeastern University London Academic Quality Framework
None
Special Provisions for Professional Statutory And Regulatory Body
None
Quality Evaluation and Enhancement
Review and Evaluation Mechanisms
The University has robust procedures, as described in AQF4 Programme and Course Approval and Modifications and AQF5 Annual Monitoring and Reporting, in place to assure the quality of the programme development, delivery, and management, alongside systematic monitoring, ongoing review and enhancement of all University programmes. Enhancements are made as necessary to ensure that systems remain effective and rigorous.
The University utilises constructive feedback from a variety of sources, internal and external, to inform its decision-making process to enhance the programme and the student experience. These feedback sources are:
- Annual Course Reviews, written by the Course Leader, are prepared to enable the Course Leader to reflect on the course, using a variety of data and student/faculty feedback to enhance the course and support the writing of the Annual Programme Review.
- Annual Programme Reviews, written at the end of each academic year, are prepared in order to enhance individual programmes and to plan ahead.
- Annual External Examiner Reports are prepared by the External Examiners, as appointed by the University, to confirm that a programme has been assessed in accordance with the approved documentation and that the student performance meets the appropriate academic standards.
- Formal learner feedback mechanisms consist of course and programme learner satisfaction questionnaires and Learner Voice Committee.
- Informal learner feedback is also valued by the University and this can take the form of learners talking to their success manager (which incorporates the personal tutor role), faculty, professional staff, or elected learner representative.
In addition to academic progress monitoring, progression also includes checking that the learner is achieving planned levels of off-the-job learning required by the apprenticeship as set out in the apprenticeship training plan. This eight-weekly discussion between the success manager, line manager and learner will also confirm whether the learner is keeping pace with their plan of learning at work, and is meeting the competency progression points as part of their apprenticeship.
Learner attendance at scheduled learning opportunities, as well as monitoring periods of off-the-job training, is monitored through the use of an online Learner Management System.
Version History
| Title: BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (Software Engineer)
BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (IT Consultant) BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (Business Analyst) BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (Cyber Security Specialist) BSc (Hons) Digital and Technology Solutions (Data Analyst) Approved by: Academic Board Location: Academic Handbook/BSc (Hons) Digital & Technology Solutions |
|||||
| Version number | Date approved | Date published | Faculty Director | Proposed next review date | Modification (As per AQF4) & category number |
| 4.0 | October 2023 | October 2023 | Dr Alexandros Koliousis | August 2028 | Category 3: Regulatory change |
| 3.0 | October 2022 | October 2022 | Professor Scott Wildman | April 2025 | Category 2: Regulatory change
Category 1: Corrections/clarifications to documents which do not change approved content or learning outcomes |
| 2.0 | July 2022 | September 2022 | Professor Scott Wildman | April 2025 | Category 3: Addition of two specialisms |
| 1.2 | April 2022 | April 2022 | Professor Scott Wildman | April 2025 | Category 1: Corrections/clarifications to documents which do not change approved content. |
| 1.1 | January 2021 | January 2021 | Professor Scott Wildman | April 2025 | Category 1: Corrections/clarifications to documents which do not change approved content. |
| 1.0 | June 2020 | June 2020 | Professor Scott Wildman | April 2025 | |
| Referenced documents | Recognition of Prior Learning and Credit Transfer Policy; AQF4 Programme and Course Approval and Modifications; AQF5 Annual Monitoring and Reporting | ||||
| External Reference Point(s) | Digital and Technology Solutions Professional (Integrated Degree) ST0119; Computing (October 2019); Education Skills and Funding Agency (ESFA) Funding Rules; Institute for Apprenticeships & Technical Education Assessment Plan; QAA (Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education) Code of Practice for the Assurance of Academic Quality and Standards in Higher Education | ||||
Disclaimer
The University has checked the information provided in this Programme Specification and will aim to deliver this programme in keeping with this Programme Specification.
However, changes to the programme may sometimes be required arising from annual monitoring, student feedback, and the review and update of courses and programmes. Where this activity leads to significant changes to courses and programmes there will be prior consultation with students and others, wherever possible, and the University will take all reasonable steps to minimise disruption to students. It is also possible that the University may not be able to offer a course or programme for reasons outside of its control, for example, due to the absence of a member of staff or low student registration numbers. Where this is the case, the University will aim to inform applicants and students as soon as possible, and where appropriate, will facilitate the transfer of affected students to another suitable programme.
Copyright
The contents of this Programme Specification are the copyright of the University and all rights are reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, such as electronic, mechanical, photocopied, recorded or otherwise, without the prior consent of the University.
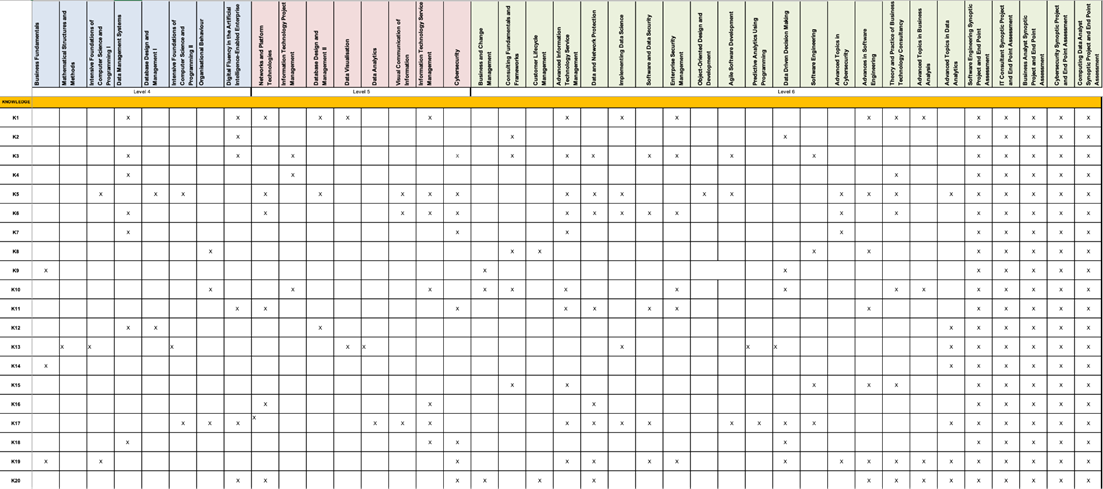
Appendix A – Map to QAA Subject Benchmark
| Threshold Standards | Learning Outcome |
| Demonstrate a requisite understanding of the main body of knowledge for their study. | K1-4
S1-4 |
| Understand and apply essential concepts, principles and practices of the subject in the context of well-defined scenarios, showing judgement in the selection and application of tools and techniques. | K1-4 S1-4 |
| Be able to demonstrate judgement, critical thinking and problem-solving skills to solve well-specified problems, to create computational artefacts with a degree of independence | K1-4
S1-4 T3-4 |
| Demonstrate the ability to undertake problem identification and analysis to appropriately design, develop, test, integrate or deploy a computing system and any associated artefacts; understand the relationship between stages | K1-4
S1-4 |
| Demonstrate the ability to work in an effective manner, including as a member of a team, making use of tools and techniques to appropriately communicate, manage tasks and plan projects under guidance | T1-4 |
| Identify appropriate practices and perform work within a professional, legal and ethical framework – including data management and use, security, equality, diversity and inclusion (EDI) and sustainability – in the work that they undertake. | K1-4 S1-4
T2-3 |
* This is intended to mean that all learners (taken over all years) graduating with an honours degree in this discipline will have achieved this.
QAA benchmark (Computing – March 2022) statement can be found here.
Appendix B – Map to Apprenticeship Standard
| Knowledge and Understanding | K1a | K1b | K1c | K2a | K2b | K2c | K3a | K3b | K3c | K4a | K4b | K4c |
| FHEQ Level 4 | ||||||||||||
| Business Fundamentals | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Mathematical Structures and Methods | X | |||||||||||
| Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming I | X | X | ||||||||||
| Data Management Systems | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Database Design and Management I | X | X | ||||||||||
| Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming II | X | X | ||||||||||
| Organisational Behaviour | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Digital Fluency in the Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Enterprise | X | X | ||||||||||
| FHEQ Level 5 | ||||||||||||
| Information Technology Project Management | X | X | ||||||||||
| Database Design and Management II | X | X | ||||||||||
| Data Analytics | X | X | ||||||||||
| Data Visualisation | X | X | ||||||||||
| Visual Communication of Information | X | X | ||||||||||
| Information Technology Service Management | X | X | ||||||||||
| Cyber Security | X | X | ||||||||||
| Networks and Platform Technologies | X | X | X | |||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Software Engineer Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Object-Oriented Design and Development | X | X | ||||||||||
| Software Engineering | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Software and Data Security | X | X | ||||||||||
| Agile Software Development | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Advances in Software Engineering | X | X | X | |||||||||
| DTSP Software Engineer End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (IT Consultant Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Consulting Fundamentals and Frameworks | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Customer Lifecycle Management | X | |||||||||||
| Advanced Information Technology Service Management | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Business and Change Management | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Theory and Practice of Business Technology Consultancy | X | X | X | |||||||||
| DTSP IT Consultant End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Business Analyst Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Consulting Fundamentals and Frameworks | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Software Engineering | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Predictive Analytics Using Programming | X | |||||||||||
| Business and Change Management | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Advanced Topics in Business Analysis | X | X | X | |||||||||
| DTSP Business Analyst End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Cyber Security Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Data and Network Protection | X | |||||||||||
| Software Engineering | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Software and Data Security | X | X | ||||||||||
| Enterprise Security Management | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Advanced Topics in Cyber Security | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| DTSP Cyber Security Analyst End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Data Analyst Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Data Driven Decision Making | X | |||||||||||
| Predictive Analytics Using Programming | X | X | ||||||||||
| Implementing Data Science | X | X | ||||||||||
| Advanced Topics in Data Analytics | X | X | ||||||||||
| DTSP Data Analyst End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
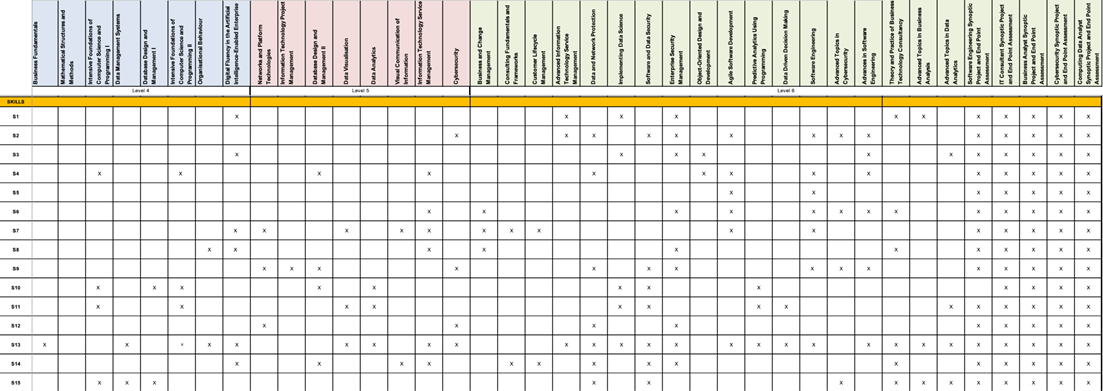
| Subject Specific Skills | S1a | S1b | S1c | S2a | S2b | S2c | S3a | S3b | S3c | S4a | S4b | S4c |
| FHEQ Level 4 | ||||||||||||
| Business Fundamentals | X | |||||||||||
| Mathematical Structures and Methods | X | |||||||||||
| Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming I | X | X | ||||||||||
| Data Management Systems | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Database Design and Management I | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming II | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Organisational Behaviour | X | |||||||||||
| Digital Fluency in the Artificial Intelligence- Enabled Enterprise | X | |||||||||||
| FHEQ Level 5 | ||||||||||||
| Information Technology Project Management | X | X | ||||||||||
| Database Design and Management II | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Data Analytics | X | |||||||||||
| Data Visualisation | X | X | ||||||||||
| Visual Communication of Information | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Information Technology Service Management | X | |||||||||||
| Cyber Security | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Networks and Platform Technologies | X | X | X | |||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Software Engineer Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Object-Oriented Design and Development | X | |||||||||||
| Software Engineering | X | |||||||||||
| Software and Data Security | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Agile Software Development | X | X | ||||||||||
| Advances in Software Engineering | X | X | ||||||||||
| DTSP Software Engineer End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (IT Consultant Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Consulting Fundamentals and Frameworks | ||||||||||||
| Customer Life cycle Management | ||||||||||||
| Advanced Information Technology Service Management | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Business and Change Management | X | X | ||||||||||
| Theory and Practice of Business Technology Consultancy | X | X | ||||||||||
| DTSP IT Consultant End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Business Analyst Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Consulting Fundamentals and Frameworks | X | |||||||||||
| Software Engineering | X | |||||||||||
| Predictive Analytics Using Programming | X | |||||||||||
| Business and Change Management | X | X | ||||||||||
| Advanced Topics in Business Analysis | X | X | ||||||||||
| DTSP Business Analyst End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Cyber Security Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Data and Network Protection | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Software Engineering | X | |||||||||||
| Software and Data Security | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Enterprise Security Management | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Advanced Topics in Cyber Security | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| DTSP Cyber Security Analyst End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Data Analyst Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Data Driven Decision Making | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Predictive Analytics Using Programming | X | |||||||||||
| Implementing Data Science | X | |||||||||||
| Advanced Topics in Data Analytics | X | X | ||||||||||
| DTSP Data Analyst End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
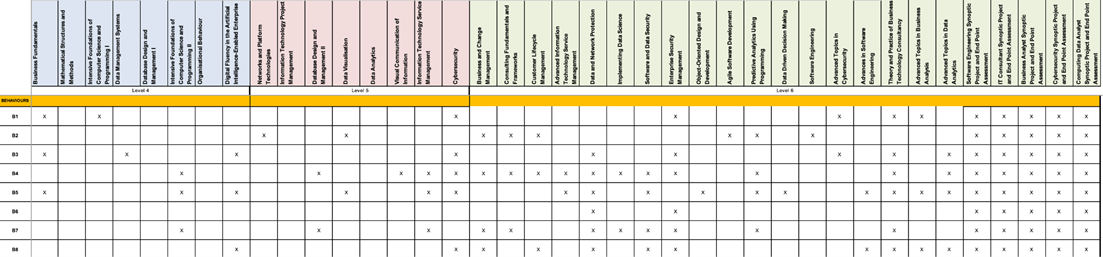
| Transferable and Professional Skills | T1a | T1b | T1c | T2a | T2b | T2c | T3a | T3b | T3c | T4a | T4b | T4c |
| FHEQ Level 4 | ||||||||||||
| Business Fundamentals | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Mathematical Structures and Methods | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming I | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Data Management Systems | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Database Design and Management I | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming II | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Organisational Behaviour | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Digital Fluency in the Artificial Intelligence- Enabled Enterprise | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 5 | ||||||||||||
| Information Technology Project Management | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Database Design and Management II | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Data Analytics | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Data Visualisation | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Visual Communication of Information | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Information Technology Service Management | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Cyber Security | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Networks and Platform Technologies | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Software Engineer Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Object-Oriented Design and Development | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Software Engineering | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Software and Data Security | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Agile Software Development | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Advances in Software Engineering | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| DTSP Software Engineer End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (IT Consultant Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Consulting Fundamentals and Frameworks | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Customer Lifecycle Management | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Advanced Information Technology Service Management | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Business and Change Management | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Theory and Practice of Business Technology Consultancy | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| DTSP IT Consultant End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Business Analyst Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Consulting Fundamentals and Frameworks | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Software Engineering | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Predictive Analytics Using Programming | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Business and Change Management | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Advanced Topics in Business Analysis | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| DTSP Business Analyst End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Cyber Security Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Data and Network Protection | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Software Engineering | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Software and Data Security | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Enterprise Security Management | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Advanced Topics in Cyber Security | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| DTSP Cyber Security Analyst End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| FHEQ Level 6 (Data Analyst Specialism) | ||||||||||||
| Data Driven Decision Making | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Predictive Analytics Using Programming | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Implementing Data Science | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Advanced Topics in Data Analytics | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| DTSP Data Analyst End-Point Assessment | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
Appendix C – Map to Apprenticeship Standard
Core KSB
Software Engineering Specialism
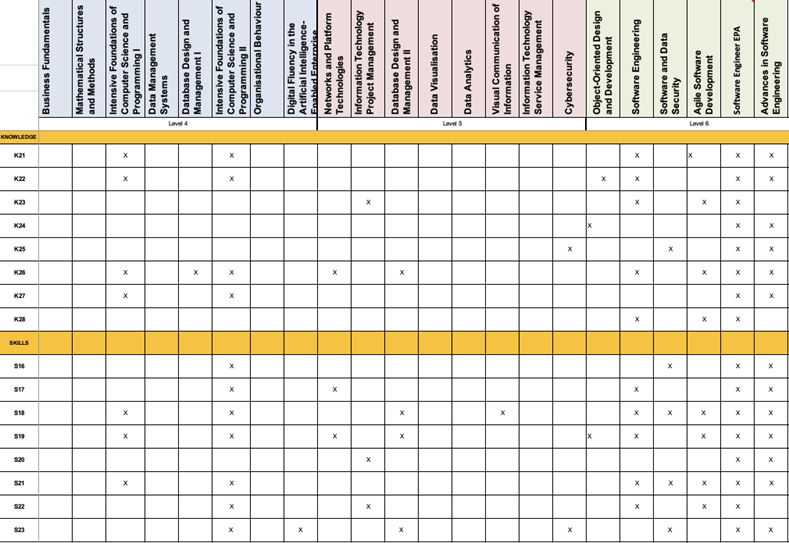
IT Consultant Specialism
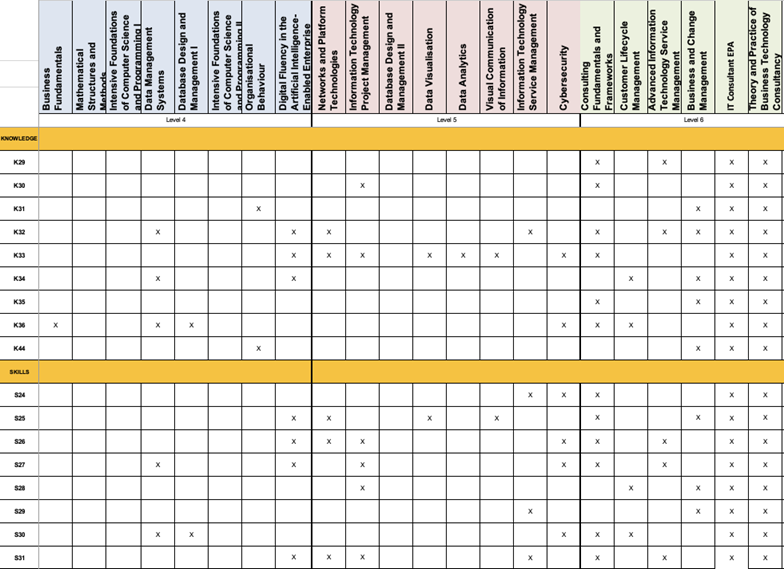
Business Analyst
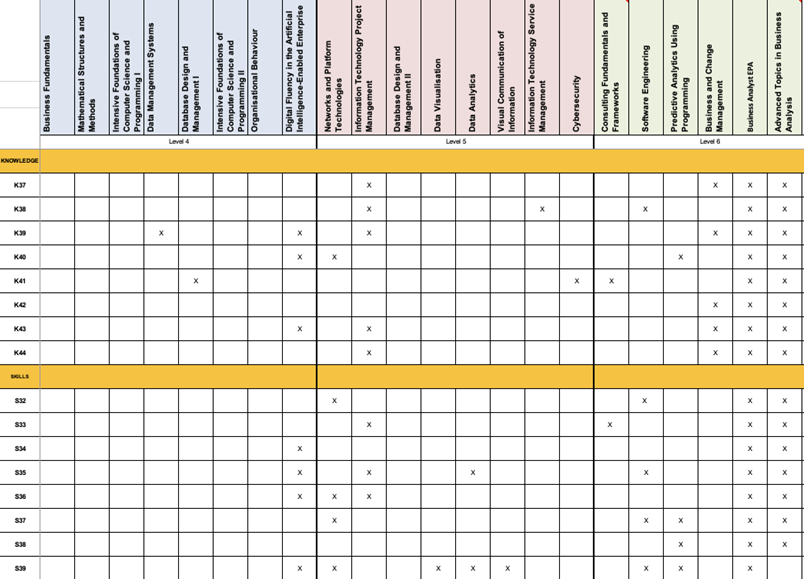
Cyber Security Specialism
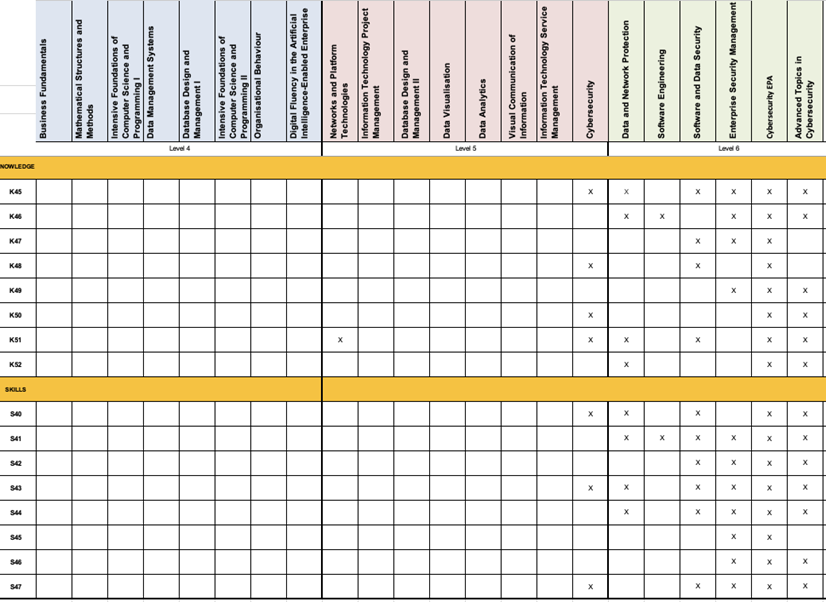
Data Analysis Specialism
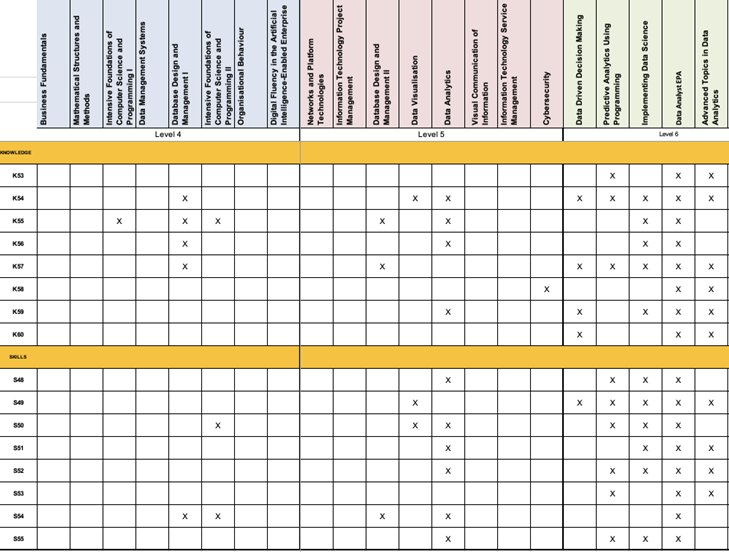
Appendix D – Programme Structure and Summative Assessment Summary
| Code | Recommended Order | Course Title | Credit | Type | Mode | Assessment Weighting % & Activity Type (code overleaf) |
|||
| AE1 | Activity
type |
AE2 | Activity type | ||||||
| FHEQ Level 4 | |||||||||
| NCHNAP443 | 1 | Business Fundamentals | 15 | C | DL/WB | 50% | A | 50% | A |
| NCHNAP445 | 2 | Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming I | 15 | C | DL/WB | 50% | Set | 50% | Pract |
| NCHNAP444 | 3 | Mathematical Structures and Methods | 15 | C | DL/WB | 60% | Set | 40% | CBEx |
| NCHNAP446 | 4 | Data Management Systems | 15 | C | DL/WB | 70% | A | 30% | CBEx |
| NCHNAP447 | 5 | Database Design and Management I | 15 | C | DL/WB | 60% | Set | 40% | R |
| NCHNAP448 | 6 or 7 | Intensive Foundations of Computer Science and Programming II | 15 | C | DL/WB | 50% | Set | 50% | R |
| NCHNAP449 | 7 or 8 | Organisational Behaviour | 15 | C | DL/WB | 60% | A | 40% | A |
| LCSCI4273A
|
8 or 6 | Digital Fluency in the Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Enterprise | 15 | C | BK/BL | 70% | A | 30% | Oral |
| FHEQ Level 5 | |||||||||
| NCHNAP555 | 9 | Information Technology Project Management | 15 | C | DL/WB | 70% | A | 30% | CBEx |
| NCHNAP556 | 10 | Database Design and Management II | 15 | C | DL/WB | 60% | Pract | 40% | Set |
| NCHNAP558 | 11 | Data Analytics | 15 | C | DL/WB | 60% | Pract | 40% | A |
| LCSCI52100A | 12 | Cyber Security | 15 | C | DL/WB | 50% | A | 50% | A |
| NCHNAP560 | 13 | Information Technology Service Management | 15 | C | DL/WB | 70% | R | 30% | CBEx |
| NCHNAP559 | 14 or 15 | Visual Communication of Information | 15 | C | DL/WB | 70% | Pract | 30% | A |
| NCHNAP557 | 15 or 16 | Data Visualisation | 15 | C | DL/WB | 70% | Pract | 30% | A |
| LCSCI5299A | 16 or 14 | Networks and Platform Technologies | 15 | C | BK/BL | 70% | A | 30% | Oral |
| FHEQ Level 6 | |||||||||
| NCHNAP6140 | 17 | Object-Oriented Design and Development | 15 | C for Software Engineer | DL/WB | 60% | Set | 40% | A |
| NCHNAP685 | 17 | Consulting Fundamentals and Frameworks | 15 | C for IT Consultant or Business Analyst | DL/WB | 70% | A | 30% | Set |
| LCSCI62117A | 17 | Data and Network Protection | 15 | C for Cyber Security Analyst | DL/WB | 60% | Set | 40% | A |
| LDSCI62115A | 17&18 | Data Driven Decision Making | 30 | C for Data Analyst | DL/WB | 70% | R | 30% | A |
| NCHNAP688 | 18 | Software Engineering | 15 | C for Business Analyst or Cyber Security Analyst or Software Engineer | DL/WB | 60% | R | 40% | A |
| LISYS62113A | 18 | Customer Life Cycle Management | 15 | C for IT Consultant | DL/WB | 50% | A | 50% | A |
| NCHNAP6141 | 19 | Software and Data Security | 15 | C for Cyber Security Analyst or Software Engineer | DL/WB | 60% | Set | 40% | A |
| LCSCI62114A | 19 | Predictive Analytics Using Programming | 15 | C for Business Analyst or Data Analyst | DL/WB | 60% | A | 40% | Set
|
| NCHNAP687 | 19 | Advanced Information Technology Service Management | 15 | C for IT Consultant | DL/WB | 70% | A | 30% | CBEx |
| LISYS62112A | 20 | Business and Change Management | 15 | C for IT Consultant or Business Analyst | DL/WB | 70% | A | 30% | A |
| NCHNAP6139 | 20 | Agile Software Development | 15 | C for Software Engineer | DL/WB | 60% | A | 40% | Set |
| LISYS62116A | 20 | Enterprise Security Management | 15 | C for Cyber Security Analyst | DL/WB | 60% | Set | 40% | A |
| NCHNAP691 | 20 | Implementing Data Science | 15 | C for Data Analyst | DL/WB | 70% | A | 30% | Oral |
| LCSCI62106A | 21 | Advances in Software Engineering | 30 | C for Software Engineer | DL/WB | 40% | R | 60% | A |
| LISYS62107A | 21 | Theory and Practice of Business Technology Consultancy | 30 | C for IT Consultant | DL/WB | 20% | Oral | 80% | R |
| LCSCI62105A | 21 | Advanced Topics in Cyber Security | 30 | C for Cyber Security Analyst | DL/WB | 60% | Prac | 40% | A |
| LISYS62104A | 21 | Advanced Topics in Business Analysis | 30 | C for Business Analyst | DL/WB | 20% | Oral | 80% | R |
| LDSCI62103A | 21 | Advanced Topics in Data Analytics | 30 | C for Data Analyst | DL/WB | 60% | Prac | 40% | A |
| LSCI62119A | 22 | DTSP Software Engineer End-Point Assessment | 30 | C for Software Engineer | DL/WB | 50% | R | 50% | Oral |
| LISYS62111A | 22 | DTSP IT Consultant End-Point Assessment | 30 | C for IT Consultant | DL/WB | 50% | R | 50% | Oral |
| LCSCI62109A | 22 | DTSP Cyber Security Analyst End-Point Assessment | 30 | C for Cyber Security Analyst | DL/WB | 50% | R | 50% | Oral |
| LISYS62108A | 22 | DTSP Business Analyst End-Point Assessment | 30 | C for Business Analyst | DL/WB | 50% | R | 50% | Oral |
| LISYS62110A | 22 | DTSP Data Analyst End-Point Assessment | 30 | C for Data Analyst | DL/WB | 50% | R | 50% | Oral |
COURSE TYPE: C = Core; O = Option
COURSE MODE: CD = Campus Delivery; BK = Block Delivery; BL = Blended Learning; DL
= Distance Learning and Self-Directed Learning; EL = E-Learning; EX = Experiential; PL = Placement; WB = Work Based Learning
ASSESSMENT WEIGHTING: AE1 = Assessment Element 1; AE2 = Assessment Element 2; AE3 = Assessment Element 3;
AE4 = Assessment Element 4
| ASSESSMENT ACTIVITY TYPE | CODE |
| Written exam | Exam |
| Computer-based exam | CBEx |
| Written assignment | A |
| Report | R |
| Dissertation | Diss |
| Portfolio | F |
| Project output (other than dissertation) | P |
| Oral assessment and presentation | Oral |
| Practical skills assessment | Pract |
| Set exercise | Set |
Appendix E – Exit Awards
Certificate of Higher Education
In order for a learner to be awarded a Certificate of Higher Education (CertHE), they are required to have achieved 120 Level 4 Credits, in accordance with the Academic Regulations for Taught Awards.
Knowledge and Understanding
A learner will be able to:
K1a Discuss the various roles, functions and activities related to technology solutions within a business or organisation.
K2a Describe how strategic decisions are made in organisations.
K3a Describe the process for design, development, testing, correcting, deploying and documenting technology solutions.
K4a Describe the concepts and applications of management information systems.
Subject Specific Skills
A learner will be able to:
S1a Review a business domain/organisation in order to identify the role of information systems.
S2a Apply fundamental techniques for information and data management.
S3a Recognise cyber security risks for simple IT systems.
S4a Recognise the key elements of computer networks.
Transferable and Professional Skills
A learner will be able to:
T1a Communicate issues/solutions effectively.
T2a Respect different working styles and capabilities, to work effectively with others.
T3a Appreciate feedback and reflect on their own practice.
T4a Display problem-solving skills.
Diploma of Higher Education
In order for a learner to be awarded a Diploma of Higher Education (DipHE), they are required to have achieved 120 Level 4 Credits and 120 Level 5 Credits, in accordance with the Academic Regulations for Taught Awards.
Knowledge and Understanding
A learner will be able to:
K1b Explain the various roles, functions and activities related to technology solutions within a business or organisation, with knowledge of how business invests in technology solutions.
K2b Explain how strategic decisions are made concerning acquiring technology solutions resources and capabilities including the ability to analyse and evaluate the different sourcing options.
K3b Evaluate the techniques for design, development, testing, correcting, deploying and documenting technology solutions from specifications.
K4b Discuss and comment upon management systems in managing organisational data and information, and how teams work effectively to produce technology solutions.
Subject Specific Skills
A learner will be able to:
S1b Analyse a business domain/organisation in order to identify the role of information systems and identify areas for improvement.
S2b Identify organisational information requirements, including industry-standard database management systems.
S3b Apply cyber security risk assessments for simple IT systems.
S4c Explain and plan computer networks in relation to the services and capabilities.
Transferable and Professional Skills
A learner will be able to:
T1b Communicate effectively issues/solutions while demonstrating basic business knowledge.
T2b Respect different working styles and capabilities, including neurodivergent needs and competing interests within and outside the organisation.
T3b Receive feedback constructively and incorporate it into their own development.
T4b Apply analytical and problem-solving skills.
Footnotes
1A learner must be in a role that provides the opportunities to gain the knowledge, skills and
behaviours needed to achieve their apprenticeship; i.e. a pathway to a competent Digital and
Technology Solutions Professional (DTSP). A DTSP provides technology enabled solutions to internal
and/or external customers, in a range of areas including software, business and systems analysis,
cyber security, data analysis and network infrastructure. They implement technology solutions that
enable businesses to develop new products and services and to increase an organisations
productivity using digital technologies. They are confident, competent and capable independent
Digital and Technology Solutions Professionals able to operate in a range of related roles.
